言語サーバー拡張機能ガイド
プログラムによる言語機能のトピックで見たように、languages.* API を直接使用して言語機能を実装することは可能です。しかし、言語サーバー拡張機能は、そのような言語サポートを実装する別の方法を提供します。
このトピックでは
- 言語サーバー拡張機能の利点を説明します。
Microsoft/vscode-languageserver-nodeライブラリを使用して言語サーバーを構築する方法を説明します。または、lsp-sampleで直接コードにアクセスすることもできます。
なぜ言語サーバーなのか?
言語サーバーは、多くのプログラミング言語の編集エクスペリエンスを強化する特殊な種類の Visual Studio Code 拡張機能です。言語サーバーを使用すると、オートコンプリート、エラーチェック (診断)、定義へのジャンプ、その他 VS Code でサポートされている多くの言語機能を実装できます。
しかし、VS Code で言語機能のサポートを実装する際に、3つの共通の問題が見つかりました。
まず、言語サーバーは通常、ネイティブのプログラミング言語で実装されており、Node.js ランタイムを持つ VS Code と統合する上で課題が生じます。
さらに、言語機能はリソースを大量に消費する可能性があります。たとえば、ファイルを正しく検証するには、言語サーバーは大量のファイルを解析し、それらの抽象構文木を構築し、静的プログラム解析を実行する必要があります。これらの操作は、かなりの CPU およびメモリ使用量を発生させる可能性があり、VS Code のパフォーマンスが影響を受けないようにする必要があります。
最後に、複数の言語ツールを複数のコードエディタと統合するには、かなりの労力が必要です。言語ツールの観点からは、異なる API を持つコードエディタに適応する必要があります。コードエディタの観点からは、言語ツールから一様な API を期待することはできません。これにより、N 個のコードエディタでM 個の言語の言語サポートを実装するには、M * N の作業が必要になります。
これらの問題を解決するために、Microsoft は、言語ツールとコードエディタ間の通信を標準化するLanguage Server Protocol を規定しました。このようにして、言語サーバーは任意の言語で実装でき、言語サーバープロトコルを介してコードエディタと通信するため、パフォーマンスコストを回避するために独自のプロセスで実行できます。さらに、LSP 準拠の任意の言語ツールは複数の LSP 準拠のコードエディタと統合でき、LSP 準拠の任意のコードエディタは複数の LSP 準拠の言語ツールを簡単に利用できます。LSP は、言語ツールプロバイダーとコードエディタベンダーの両方にとって有利です!

このガイドでは
- 提供されているNode SDK を使用して、VS Code で言語サーバー拡張機能を構築する方法を説明します。
- 言語サーバー拡張機能の実行、デバッグ、ログ、テストの方法を説明します。
- 言語サーバーに関するいくつかの高度なトピックを紹介します。
言語サーバーの実装
概要
VS Code では、言語サーバーは2つの部分で構成されます。
- 言語クライアント: JavaScript / TypeScript で書かれた通常の VS Code 拡張機能。この拡張機能は、すべてのVS Code Namespace API にアクセスできます。
- 言語サーバー: 別のプロセスで実行される言語解析ツール。
上記で簡単に述べたように、言語サーバーを別のプロセスで実行することには2つの利点があります。
- 解析ツールは、言語サーバープロトコルに従って言語クライアントと通信できる限り、任意の言語で実装できます。
- 言語解析ツールは CPU とメモリを大量に消費することが多いため、別のプロセスで実行することでパフォーマンスコストを回避できます。
以下は、2つの言語サーバー拡張機能を実行している VS Code の図です。HTML 言語クライアントと PHP 言語クライアントは、TypeScript で書かれた通常の VS Code 拡張機能です。それぞれが対応する言語サーバーをインスタンス化し、LSP を介してそれらと通信します。PHP 言語サーバーは PHP で書かれていますが、LSP を介して PHP 言語クライアントと通信できます。
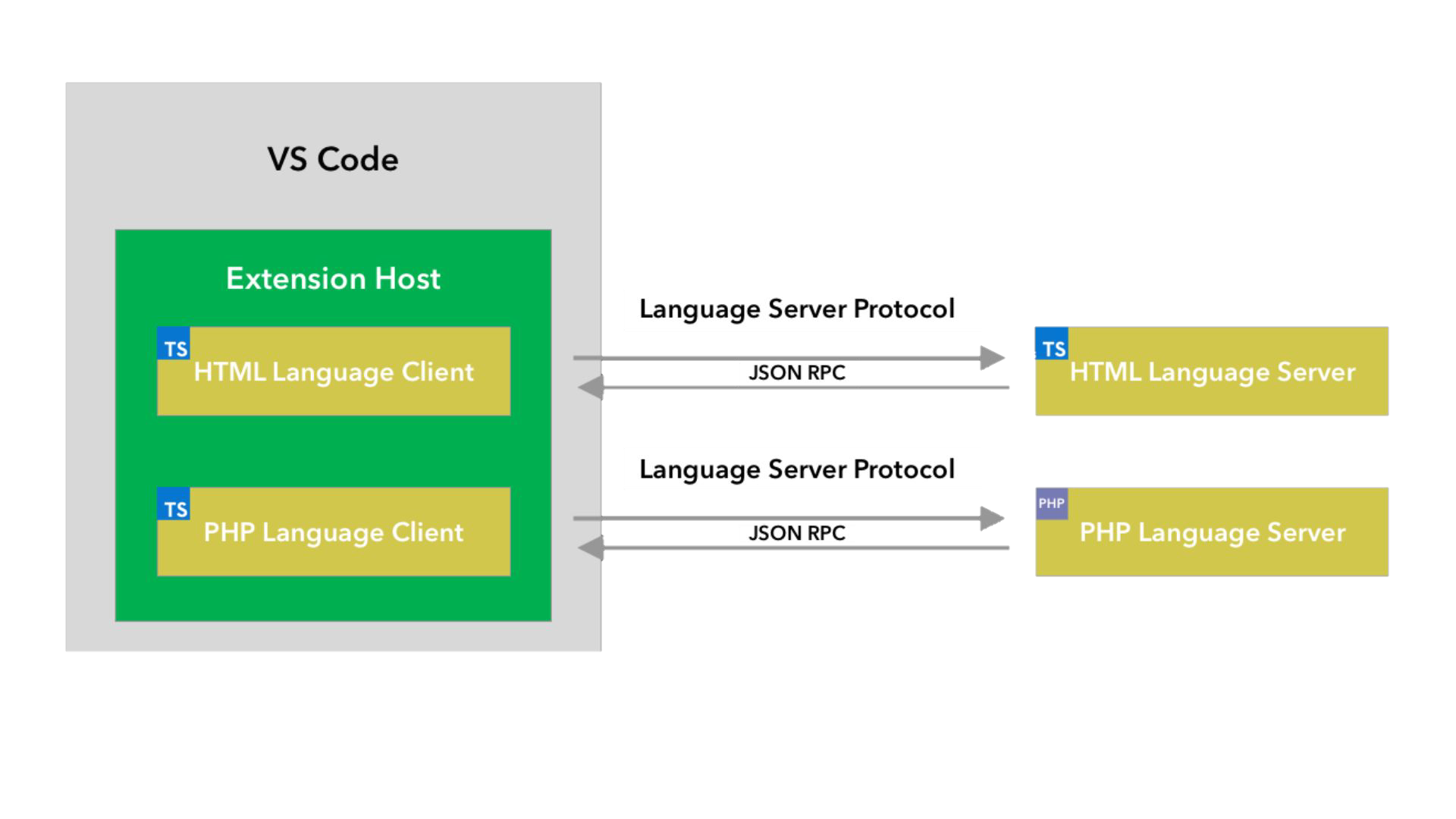
このガイドでは、Node SDK を使用して言語クライアント/サーバーを構築する方法を説明します。残りのドキュメントは、VS Code 拡張機能 API に精通していることを前提としています。
LSP サンプル - プレーンテキストファイル用のシンプルな言語サーバー
プレーンテキストファイル用のオートコンプリートと診断を実装するシンプルな言語サーバー拡張機能を構築しましょう。クライアント/サーバー間の構成の同期についても説明します。
すぐにコードにアクセスしたい場合
- lsp-sample: このガイドのための詳細なドキュメント付きソースコード。
- lsp-multi-server-sample: VS Code のマルチルートワークスペース機能をサポートするために、ワークスペースフォルダーごとに異なるサーバーインスタンスを開始する、lsp-sample の詳細なドキュメント付きの高度なバージョン。
Microsoft/vscode-extension-samples リポジトリをクローンし、サンプルを開きます。
> git clone https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-extension-samples.git
> cd vscode-extension-samples/lsp-sample
> npm install
> npm run compile
> code .
上記により、すべての依存関係がインストールされ、クライアントとサーバーの両方のコードを含む lsp-sample ワークスペースが開きます。以下は、lsp-sample の構造の概要です。
.
├── client // Language Client
│ ├── src
│ │ ├── test // End to End tests for Language Client / Server
│ │ └── extension.ts // Language Client entry point
├── package.json // The extension manifest
└── server // Language Server
└── src
└── server.ts // Language Server entry point
「言語クライアント」の説明
まず、言語クライアントの機能を記述する /package.json を見てみましょう。興味深いセクションが2つあります。
まず、configuration セクションを見てください。
"configuration": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Example configuration",
"properties": {
"languageServerExample.maxNumberOfProblems": {
"scope": "resource",
"type": "number",
"default": 100,
"description": "Controls the maximum number of problems produced by the server."
}
}
}
このセクションでは、VS Code に configuration 設定を提供します。この例では、これらの設定が起動時と設定の変更ごとに言語サーバーに送信される方法を説明します。
注意: 拡張機能が VS Code バージョン 1.74.0 より前のバージョンと互換性がある場合、プレーンテキストファイル (たとえば拡張子
.txtのファイル) が開かれるとすぐに拡張機能をアクティブ化するように VS Code に伝えるために、/package.jsonのactivationEventsフィールドにonLanguage:plaintextを宣言する必要があります。"activationEvents": []
実際の言語クライアントのソースコードと対応する package.json は /client フォルダーにあります。/client/package.json ファイルの興味深い部分は、engines フィールドを介して vscode 拡張機能ホスト API を参照し、vscode-languageclient ライブラリへの依存関係を追加していることです。
"engines": {
"vscode": "^1.52.0"
},
"dependencies": {
"vscode-languageclient": "^7.0.0"
}
前述のとおり、クライアントは通常の VS Code 拡張機能として実装されており、すべての VS Code 名前空間 API にアクセスできます。
以下は、対応する extension.ts ファイルの内容です。これは lsp-sample 拡張機能のエントリです。
import * as path from 'path';
import { workspace, ExtensionContext } from 'vscode';
import {
LanguageClient,
LanguageClientOptions,
ServerOptions,
TransportKind
} from 'vscode-languageclient/node';
let client: LanguageClient;
export function activate(context: ExtensionContext) {
// The server is implemented in node
let serverModule = context.asAbsolutePath(path.join('server', 'out', 'server.js'));
// The debug options for the server
// --inspect=6009: runs the server in Node's Inspector mode so VS Code can attach to the server for debugging
let debugOptions = { execArgv: ['--nolazy', '--inspect=6009'] };
// If the extension is launched in debug mode then the debug server options are used
// Otherwise the run options are used
let serverOptions: ServerOptions = {
run: { module: serverModule, transport: TransportKind.ipc },
debug: {
module: serverModule,
transport: TransportKind.ipc,
options: debugOptions
}
};
// Options to control the language client
let clientOptions: LanguageClientOptions = {
// Register the server for plain text documents
documentSelector: [{ scheme: 'file', language: 'plaintext' }],
synchronize: {
// Notify the server about file changes to '.clientrc files contained in the workspace
fileEvents: workspace.createFileSystemWatcher('**/.clientrc')
}
};
// Create the language client and start the client.
client = new LanguageClient(
'languageServerExample',
'Language Server Example',
serverOptions,
clientOptions
);
// Start the client. This will also launch the server
client.start();
}
export function deactivate(): Thenable<void> | undefined {
if (!client) {
return undefined;
}
return client.stop();
}
「言語サーバー」の説明
注: GitHub リポジトリからクローンされた「サーバー」実装には、最終的なウォークスルーの実装が含まれています。ウォークスルーに従うには、新しい
server.tsを作成するか、クローンされたバージョンの内容を変更してください。
この例では、サーバーも TypeScript で実装され、Node.js を使用して実行されます。VS Code にはすでに Node.js ランタイムが搭載されているため、ランタイムに特定の要件がない限り、独自のランタイムを提供する必要はありません。
言語サーバーのソースコードは /server にあります。サーバーの package.json ファイルの興味深いセクションは次のとおりです。
"dependencies": {
"vscode-languageserver": "^7.0.0",
"vscode-languageserver-textdocument": "^1.0.1"
}
これにより、vscode-languageserver ライブラリが取り込まれます。
以下は、VS Code からサーバーに常に増分デルタを送信することでテキストドキュメントを同期する、提供されているテキストドキュメントマネージャーを使用するサーバー実装です。
import {
createConnection,
TextDocuments,
Diagnostic,
DiagnosticSeverity,
ProposedFeatures,
InitializeParams,
DidChangeConfigurationNotification,
CompletionItem,
CompletionItemKind,
TextDocumentPositionParams,
TextDocumentSyncKind,
InitializeResult
} from 'vscode-languageserver/node';
import { TextDocument } from 'vscode-languageserver-textdocument';
// Create a connection for the server, using Node's IPC as a transport.
// Also include all preview / proposed LSP features.
let connection = createConnection(ProposedFeatures.all);
// Create a simple text document manager.
let documents: TextDocuments<TextDocument> = new TextDocuments(TextDocument);
let hasConfigurationCapability: boolean = false;
let hasWorkspaceFolderCapability: boolean = false;
let hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability: boolean = false;
connection.onInitialize((params: InitializeParams) => {
let capabilities = params.capabilities;
// Does the client support the `workspace/configuration` request?
// If not, we fall back using global settings.
hasConfigurationCapability = !!(
capabilities.workspace && !!capabilities.workspace.configuration
);
hasWorkspaceFolderCapability = !!(
capabilities.workspace && !!capabilities.workspace.workspaceFolders
);
hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability = !!(
capabilities.textDocument &&
capabilities.textDocument.publishDiagnostics &&
capabilities.textDocument.publishDiagnostics.relatedInformation
);
const result: InitializeResult = {
capabilities: {
textDocumentSync: TextDocumentSyncKind.Incremental,
// Tell the client that this server supports code completion.
completionProvider: {
resolveProvider: true
}
}
};
if (hasWorkspaceFolderCapability) {
result.capabilities.workspace = {
workspaceFolders: {
supported: true
}
};
}
return result;
});
connection.onInitialized(() => {
if (hasConfigurationCapability) {
// Register for all configuration changes.
connection.client.register(DidChangeConfigurationNotification.type, undefined);
}
if (hasWorkspaceFolderCapability) {
connection.workspace.onDidChangeWorkspaceFolders(_event => {
connection.console.log('Workspace folder change event received.');
});
}
});
// The example settings
interface ExampleSettings {
maxNumberOfProblems: number;
}
// The global settings, used when the `workspace/configuration` request is not supported by the client.
// Please note that this is not the case when using this server with the client provided in this example
// but could happen with other clients.
const defaultSettings: ExampleSettings = { maxNumberOfProblems: 1000 };
let globalSettings: ExampleSettings = defaultSettings;
// Cache the settings of all open documents
let documentSettings: Map<string, Thenable<ExampleSettings>> = new Map();
connection.onDidChangeConfiguration(change => {
if (hasConfigurationCapability) {
// Reset all cached document settings
documentSettings.clear();
} else {
globalSettings = <ExampleSettings>(
(change.settings.languageServerExample || defaultSettings)
);
}
// Revalidate all open text documents
documents.all().forEach(validateTextDocument);
});
function getDocumentSettings(resource: string): Thenable<ExampleSettings> {
if (!hasConfigurationCapability) {
return Promise.resolve(globalSettings);
}
let result = documentSettings.get(resource);
if (!result) {
result = connection.workspace.getConfiguration({
scopeUri: resource,
section: 'languageServerExample'
});
documentSettings.set(resource, result);
}
return result;
}
// Only keep settings for open documents
documents.onDidClose(e => {
documentSettings.delete(e.document.uri);
});
// The content of a text document has changed. This event is emitted
// when the text document first opened or when its content has changed.
documents.onDidChangeContent(change => {
validateTextDocument(change.document);
});
async function validateTextDocument(textDocument: TextDocument): Promise<void> {
// In this simple example we get the settings for every validate run.
let settings = await getDocumentSettings(textDocument.uri);
// The validator creates diagnostics for all uppercase words length 2 and more
let text = textDocument.getText();
let pattern = /\b[A-Z]{2,}\b/g;
let m: RegExpExecArray | null;
let problems = 0;
let diagnostics: Diagnostic[] = [];
while ((m = pattern.exec(text)) && problems < settings.maxNumberOfProblems) {
problems++;
let diagnostic: Diagnostic = {
severity: DiagnosticSeverity.Warning,
range: {
start: textDocument.positionAt(m.index),
end: textDocument.positionAt(m.index + m[0].length)
},
message: `${m[0]} is all uppercase.`,
source: 'ex'
};
if (hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability) {
diagnostic.relatedInformation = [
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Spelling matters'
},
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Particularly for names'
}
];
}
diagnostics.push(diagnostic);
}
// Send the computed diagnostics to VS Code.
connection.sendDiagnostics({ uri: textDocument.uri, diagnostics });
}
connection.onDidChangeWatchedFiles(_change => {
// Monitored files have change in VS Code
connection.console.log('We received a file change event');
});
// This handler provides the initial list of the completion items.
connection.onCompletion(
(_textDocumentPosition: TextDocumentPositionParams): CompletionItem[] => {
// The pass parameter contains the position of the text document in
// which code complete got requested. For the example we ignore this
// info and always provide the same completion items.
return [
{
label: 'TypeScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 1
},
{
label: 'JavaScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 2
}
];
}
);
// This handler resolves additional information for the item selected in
// the completion list.
connection.onCompletionResolve(
(item: CompletionItem): CompletionItem => {
if (item.data === 1) {
item.detail = 'TypeScript details';
item.documentation = 'TypeScript documentation';
} else if (item.data === 2) {
item.detail = 'JavaScript details';
item.documentation = 'JavaScript documentation';
}
return item;
}
);
// Make the text document manager listen on the connection
// for open, change and close text document events
documents.listen(connection);
// Listen on the connection
connection.listen();
簡単な検証の追加
サーバーにドキュメント検証を追加するには、テキストドキュメントマネージャーにリスナーを追加します。このリスナーは、テキストドキュメントの内容が変更されるたびに呼び出されます。その後、ドキュメントを検証する最適なタイミングを決定するのはサーバーの役割です。この例の実装では、サーバーはプレーンテキストドキュメントを検証し、すべて大文字の単語のすべての出現箇所にフラグを立てます。対応するコードスニペットは次のようになります。
// The content of a text document has changed. This event is emitted
// when the text document first opened or when its content has changed.
documents.onDidChangeContent(async change => {
let textDocument = change.document;
// In this simple example we get the settings for every validate run.
let settings = await getDocumentSettings(textDocument.uri);
// The validator creates diagnostics for all uppercase words length 2 and more
let text = textDocument.getText();
let pattern = /\b[A-Z]{2,}\b/g;
let m: RegExpExecArray | null;
let problems = 0;
let diagnostics: Diagnostic[] = [];
while ((m = pattern.exec(text)) && problems < settings.maxNumberOfProblems) {
problems++;
let diagnostic: Diagnostic = {
severity: DiagnosticSeverity.Warning,
range: {
start: textDocument.positionAt(m.index),
end: textDocument.positionAt(m.index + m[0].length)
},
message: `${m[0]} is all uppercase.`,
source: 'ex'
};
if (hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability) {
diagnostic.relatedInformation = [
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Spelling matters'
},
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Particularly for names'
}
];
}
diagnostics.push(diagnostic);
}
// Send the computed diagnostics to VS Code.
connection.sendDiagnostics({ uri: textDocument.uri, diagnostics });
});
診断のヒントとテクニック
- 開始位置と終了位置が同じ場合、VS Code はその位置の単語を波線で下線表示します。
- 行の終わりまで波線で下線表示したい場合は、終了位置の文字を Number.MAX_VALUE に設定します。
言語サーバーを実行するには、次の手順を実行します。
- ⇧⌘B (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+B) を押してビルドタスクを開始します。このタスクはクライアントとサーバーの両方をコンパイルします。
- 「実行」ビューを開き、「クライアントを起動」起動構成を選択し、「デバッグの開始」ボタンを押して、拡張機能コードを実行する VS Code の追加の「拡張機能開発ホスト」インスタンスを起動します。
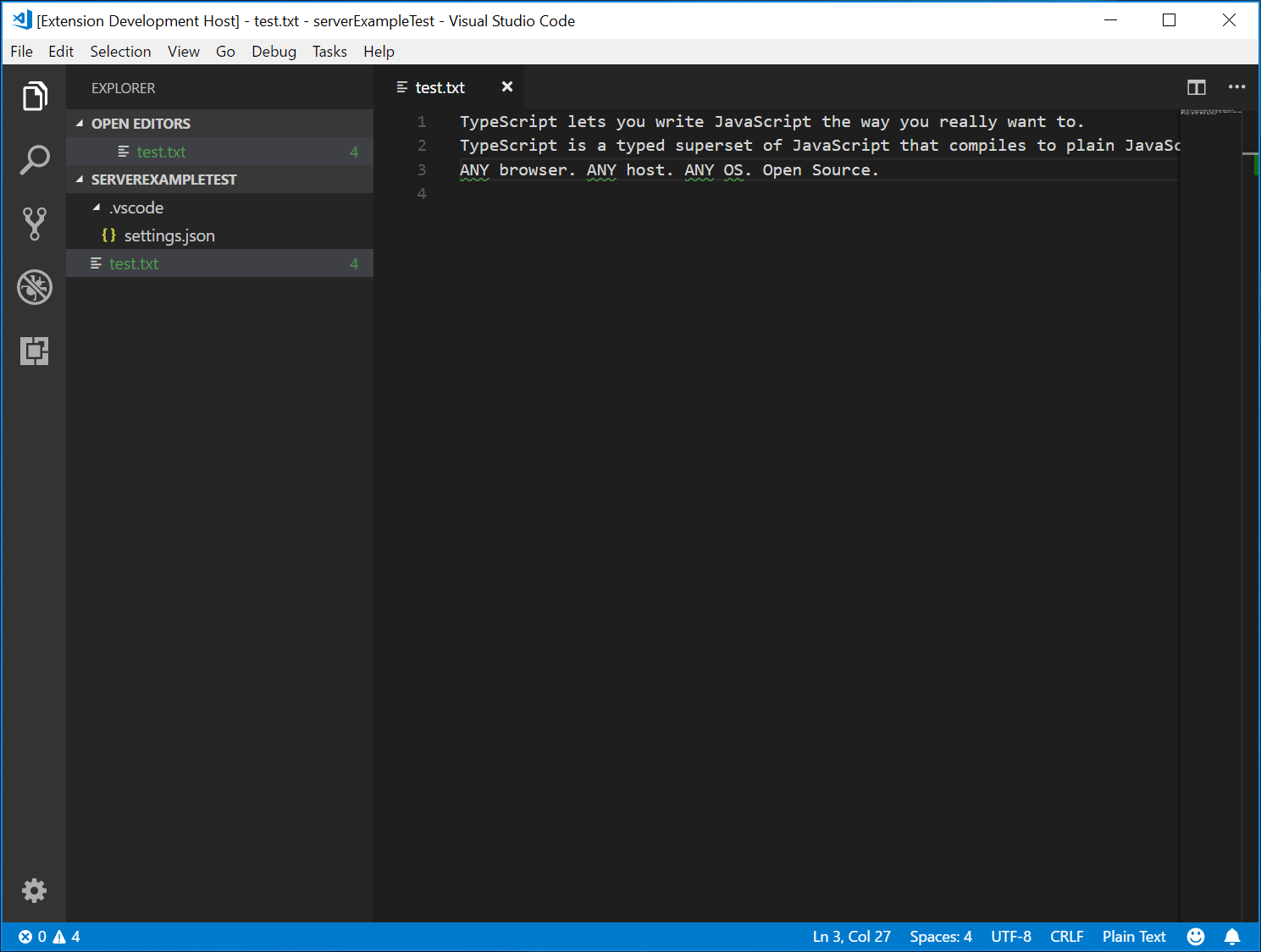
- ルートフォルダに
test.txtファイルを作成し、以下のコンテンツを貼り付けます。
TypeScript lets you write JavaScript the way you really want to.
TypeScript is a typed superset of JavaScript that compiles to plain JavaScript.
ANY browser. ANY host. ANY OS. Open Source.
「拡張機能開発ホスト」インスタンスは次のようになります。
クライアントとサーバーの両方をデバッグする
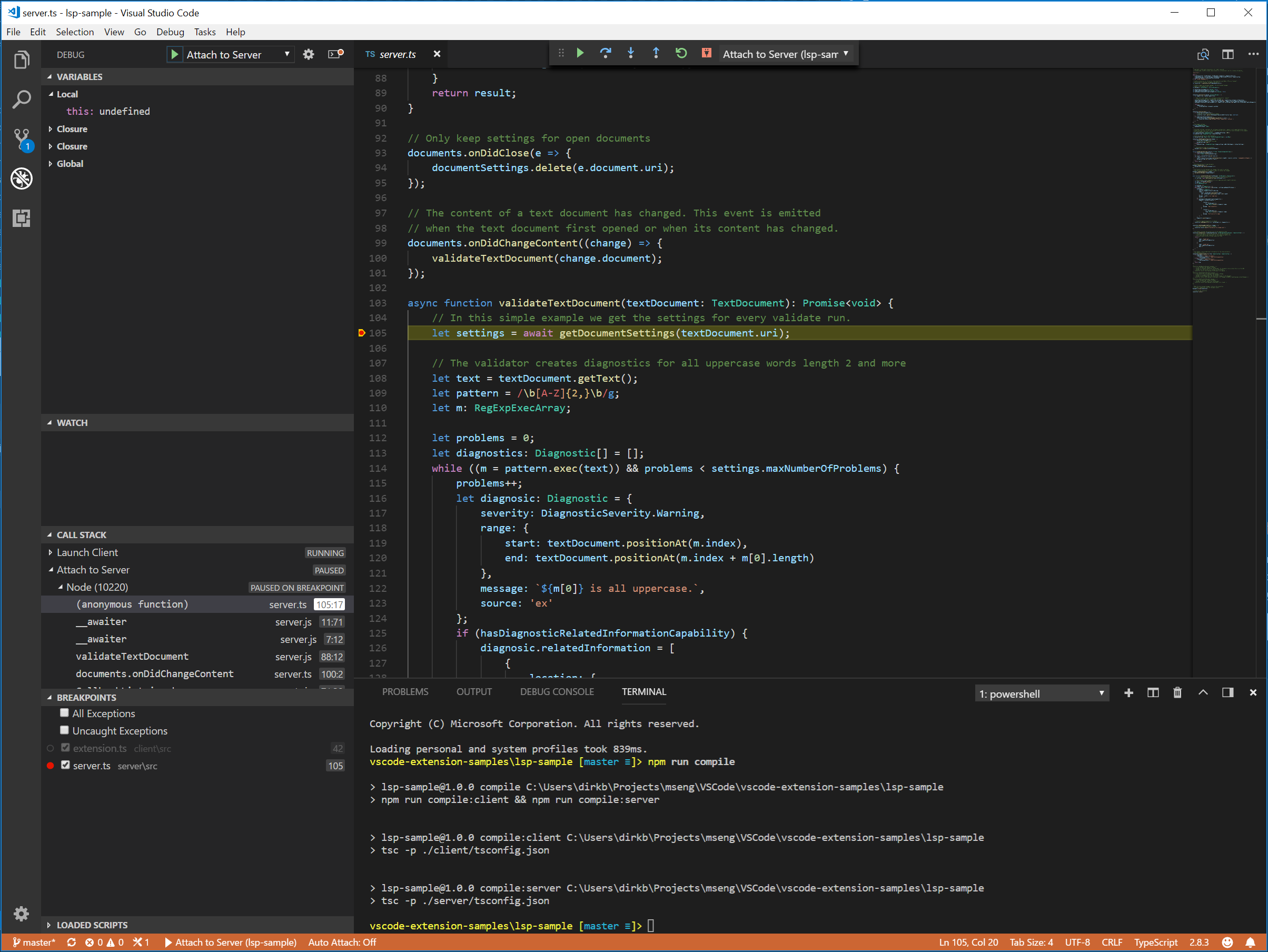
クライアントコードのデバッグは、通常の拡張機能をデバッグするのと同じくらい簡単です。クライアントコードにブレークポイントを設定し、F5 を押して拡張機能をデバッグします。

サーバーは拡張機能 (クライアント) で実行されている LanguageClient によって起動されるため、実行中のサーバーにデバッガーをアタッチする必要があります。これを行うには、「実行とデバッグ」ビューに切り替えて、「サーバーにアタッチ」起動構成を選択し、F5 を押します。これにより、デバッガーがサーバーにアタッチされます。
言語サーバーのログサポート
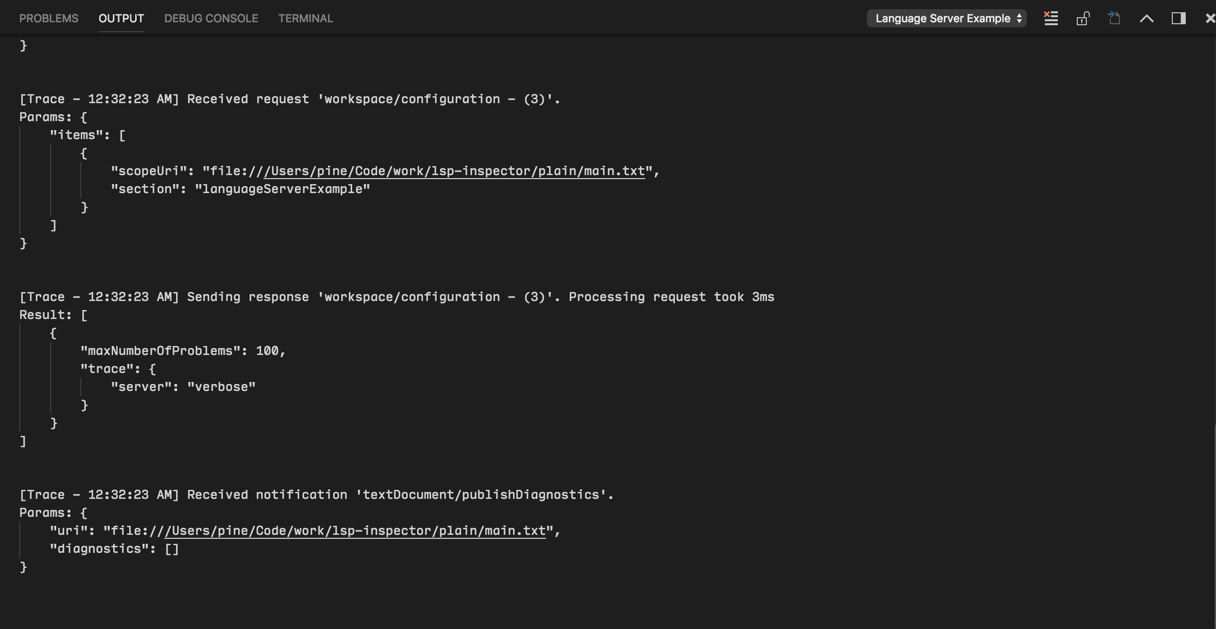
クライアントを実装するために vscode-languageclient を使用している場合、[langId].trace.server という設定を指定できます。これにより、クライアントは言語クライアント/サーバー間の通信を言語クライアントの name のチャネルにログ記録するよう指示されます。
lsp-sample の場合、この設定を "languageServerExample.trace.server": "verbose" と設定できます。次に、「Language Server Example」チャネルに移動します。ログが表示されるはずです。
サーバーでの構成設定の使用
拡張機能のクライアント部分を記述する際に、報告される問題の最大数を制御する設定をすでに定義しました。また、サーバー側でこれらの設定をクライアントから読み取るコードも記述しました。
function getDocumentSettings(resource: string): Thenable<ExampleSettings> {
if (!hasConfigurationCapability) {
return Promise.resolve(globalSettings);
}
let result = documentSettings.get(resource);
if (!result) {
result = connection.workspace.getConfiguration({
scopeUri: resource,
section: 'languageServerExample'
});
documentSettings.set(resource, result);
}
return result;
}
今必要なのは、サーバー側で構成変更をリッスンし、設定が変更された場合は開いているテキストドキュメントを再検証することだけです。ドキュメント変更イベント処理の検証ロジックを再利用できるように、コードを validateTextDocument 関数に抽出し、maxNumberOfProblems 変数を尊重するようにコードを変更します。
async function validateTextDocument(textDocument: TextDocument): Promise<void> {
// In this simple example we get the settings for every validate run.
let settings = await getDocumentSettings(textDocument.uri);
// The validator creates diagnostics for all uppercase words length 2 and more
let text = textDocument.getText();
let pattern = /\b[A-Z]{2,}\b/g;
let m: RegExpExecArray | null;
let problems = 0;
let diagnostics: Diagnostic[] = [];
while ((m = pattern.exec(text)) && problems < settings.maxNumberOfProblems) {
problems++;
let diagnostic: Diagnostic = {
severity: DiagnosticSeverity.Warning,
range: {
start: textDocument.positionAt(m.index),
end: textDocument.positionAt(m.index + m[0].length)
},
message: `${m[0]} is all uppercase.`,
source: 'ex'
};
if (hasDiagnosticRelatedInformationCapability) {
diagnostic.relatedInformation = [
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Spelling matters'
},
{
location: {
uri: textDocument.uri,
range: Object.assign({}, diagnostic.range)
},
message: 'Particularly for names'
}
];
}
diagnostics.push(diagnostic);
}
// Send the computed diagnostics to VS Code.
connection.sendDiagnostics({ uri: textDocument.uri, diagnostics });
}
構成変更の処理は、接続に構成変更の通知ハンドラを追加することで行われます。対応するコードは次のようになります。
connection.onDidChangeConfiguration(change => {
if (hasConfigurationCapability) {
// Reset all cached document settings
documentSettings.clear();
} else {
globalSettings = <ExampleSettings>(
(change.settings.languageServerExample || defaultSettings)
);
}
// Revalidate all open text documents
documents.all().forEach(validateTextDocument);
});
クライアントを再度起動し、設定を最大1つの問題報告に変更すると、次の検証結果が得られます。
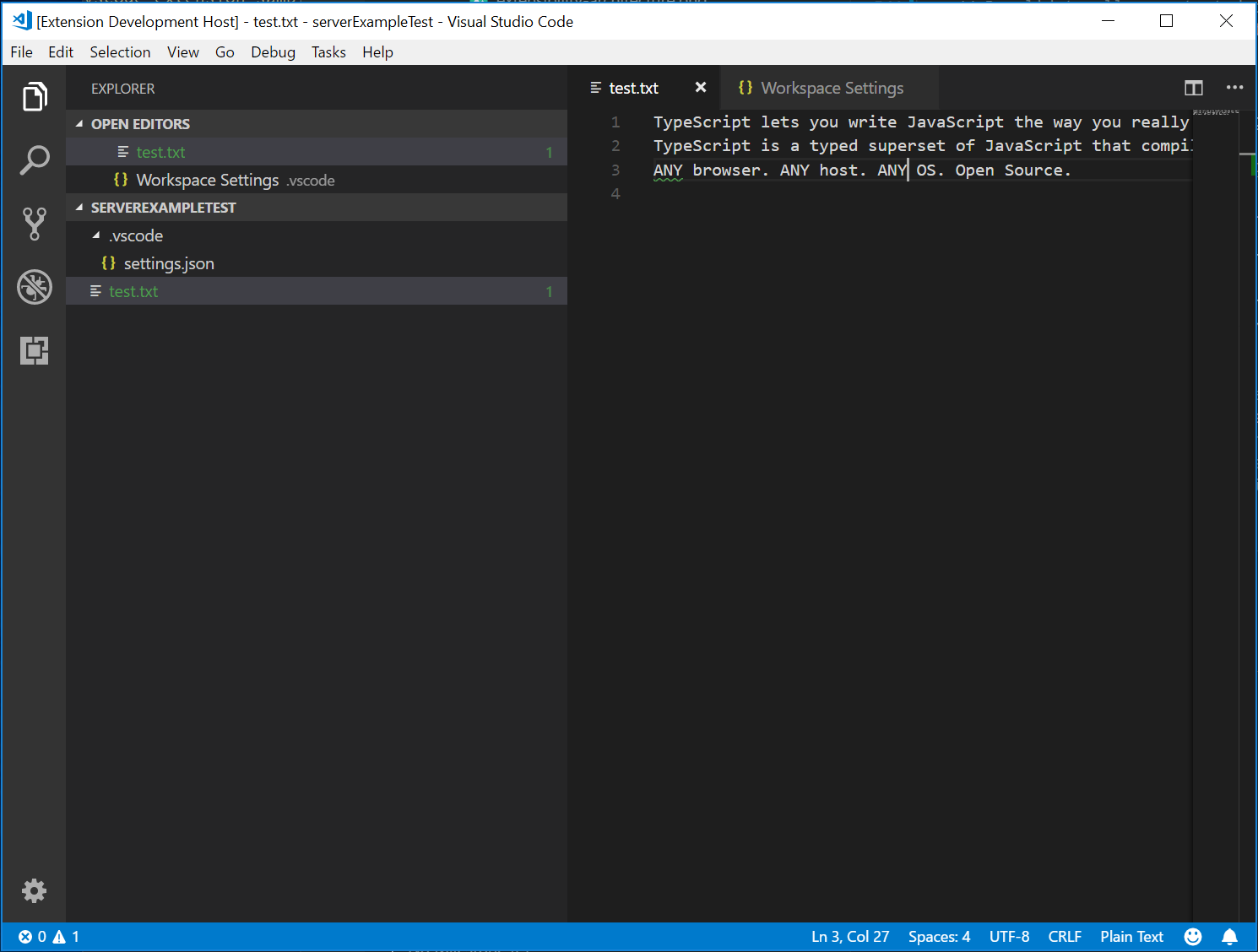
追加の言語機能の追加
言語サーバーが通常最初に実装する興味深い機能は、ドキュメントの検証です。その意味で、リンターでさえ言語サーバーと見なされ、VS Code ではリンターは通常言語サーバーとして実装されます (例としてeslintとjshintを参照)。しかし、言語サーバーには他にも多くの機能があります。コード補完、すべての参照の検索、定義への移動などを提供できます。以下の例のコードは、サーバーにコード補完を追加します。これは、「TypeScript」と「JavaScript」の2つの単語を提案します。
// This handler provides the initial list of the completion items.
connection.onCompletion(
(_textDocumentPosition: TextDocumentPositionParams): CompletionItem[] => {
// The pass parameter contains the position of the text document in
// which code complete got requested. For the example we ignore this
// info and always provide the same completion items.
return [
{
label: 'TypeScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 1
},
{
label: 'JavaScript',
kind: CompletionItemKind.Text,
data: 2
}
];
}
);
// This handler resolves additional information for the item selected in
// the completion list.
connection.onCompletionResolve(
(item: CompletionItem): CompletionItem => {
if (item.data === 1) {
item.detail = 'TypeScript details';
item.documentation = 'TypeScript documentation';
} else if (item.data === 2) {
item.detail = 'JavaScript details';
item.documentation = 'JavaScript documentation';
}
return item;
}
);
data フィールドは、解決ハンドラーで補完項目を一意に識別するために使用されます。データプロパティはプロトコルにとって透過的です。基盤となるメッセージングプロトコルは JSON ベースであるため、データフィールドには JSON にシリアル化および逆シリアル化できるデータのみを保持する必要があります。
残っているのは、VS Code にサーバーがコード補完リクエストをサポートしていることを伝えることだけです。これを行うには、初期化ハンドラーで対応する機能をフラグ付けします。
connection.onInitialize((params): InitializeResult => {
...
return {
capabilities: {
...
// Tell the client that the server supports code completion
completionProvider: {
resolveProvider: true
}
}
};
});
以下のスクリーンショットは、プレーンテキストファイルで実行されている完成したコードを示しています。
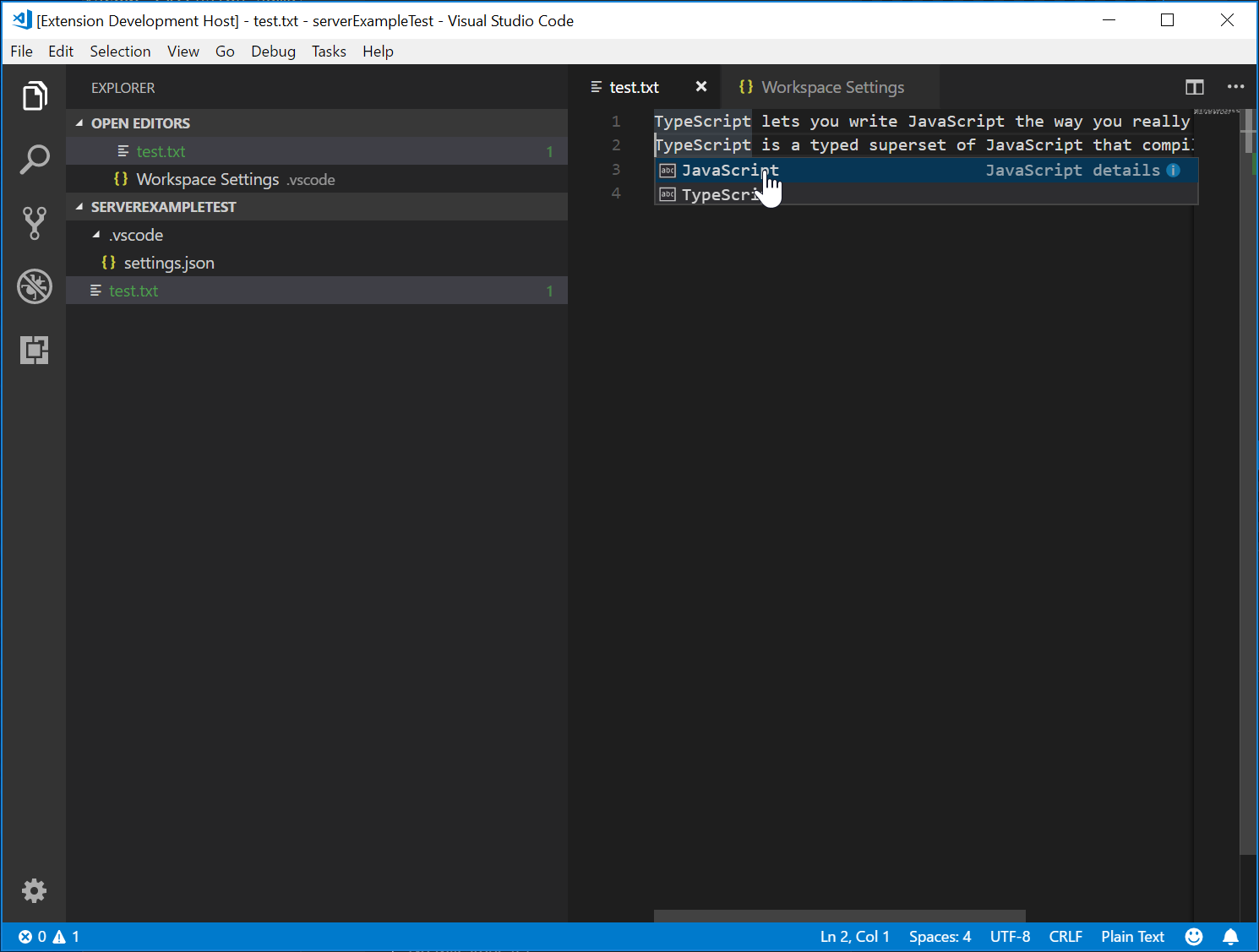
言語サーバーのテスト
高品質な言語サーバーを作成するには、その機能を網羅する優れたテストスイートを構築する必要があります。言語サーバーをテストする一般的な方法は2つあります。
- 単体テスト: これは、特定の言語サーバー機能に送信されるすべての情報をモックアップしてテストする場合に役立ちます。VS Code のHTML / CSS / JSON 言語サーバーは、このテストアプローチを採用しています。LSP npm モジュールもこのアプローチを使用しています。npm プロトコルモジュールを使用して記述されたいくつかの単体テストはこちらを参照してください。
- エンドツーエンドテスト: これはVS Code 拡張機能テストに似ています。このアプローチの利点は、ワークスペースで VS Code インスタンスをインスタンス化し、ファイルを開き、言語クライアント/サーバーをアクティブ化し、VS Code コマンドを実行することでテストを実行することです。このアプローチは、モックが困難または不可能なファイル、設定、または依存関係 (
node_modulesなど) がある場合に優れています。人気のPython 拡張機能は、このテストアプローチを採用しています。
選択した任意のテストフレームワークで単体テストを行うことは可能です。ここでは、言語サーバー拡張機能のエンドツーエンドテストを行う方法について説明します。
.vscode/launch.json を開くと、E2E テストターゲットが見つかります。
{
"name": "Language Server E2E Test",
"type": "extensionHost",
"request": "launch",
"runtimeExecutable": "${execPath}",
"args": [
"--extensionDevelopmentPath=${workspaceRoot}",
"--extensionTestsPath=${workspaceRoot}/client/out/test/index",
"${workspaceRoot}/client/testFixture"
],
"outFiles": ["${workspaceRoot}/client/out/test/**/*.js"]
}
このデバッグターゲットを実行すると、アクティブなワークスペースとして client/testFixture を持つ VS Code インスタンスが起動します。その後、VS Code は client/src/test 内のすべてのテストを実行します。デバッグのヒントとして、client/src/test 内の TypeScript ファイルにブレークポイントを設定すると、それがヒットします。
completion.test.ts ファイルを見てみましょう。
import * as vscode from 'vscode';
import * as assert from 'assert';
import { getDocUri, activate } from './helper';
suite('Should do completion', () => {
const docUri = getDocUri('completion.txt');
test('Completes JS/TS in txt file', async () => {
await testCompletion(docUri, new vscode.Position(0, 0), {
items: [
{ label: 'JavaScript', kind: vscode.CompletionItemKind.Text },
{ label: 'TypeScript', kind: vscode.CompletionItemKind.Text }
]
});
});
});
async function testCompletion(
docUri: vscode.Uri,
position: vscode.Position,
expectedCompletionList: vscode.CompletionList
) {
await activate(docUri);
// Executing the command `vscode.executeCompletionItemProvider` to simulate triggering completion
const actualCompletionList = (await vscode.commands.executeCommand(
'vscode.executeCompletionItemProvider',
docUri,
position
)) as vscode.CompletionList;
assert.ok(actualCompletionList.items.length >= 2);
expectedCompletionList.items.forEach((expectedItem, i) => {
const actualItem = actualCompletionList.items[i];
assert.equal(actualItem.label, expectedItem.label);
assert.equal(actualItem.kind, expectedItem.kind);
});
}
このテストでは
- 拡張機能をアクティブ化します。
- URI と位置を指定して
vscode.executeCompletionItemProviderコマンドを実行し、補完トリガーをシミュレートします。 - 返された補完項目を期待される補完項目に対してアサートします。
activate(docURI) 関数をもう少し詳しく見てみましょう。これは client/src/test/helper.ts で定義されています。
import * as vscode from 'vscode';
import * as path from 'path';
export let doc: vscode.TextDocument;
export let editor: vscode.TextEditor;
export let documentEol: string;
export let platformEol: string;
/**
* Activates the vscode.lsp-sample extension
*/
export async function activate(docUri: vscode.Uri) {
// The extensionId is `publisher.name` from package.json
const ext = vscode.extensions.getExtension('vscode-samples.lsp-sample')!;
await ext.activate();
try {
doc = await vscode.workspace.openTextDocument(docUri);
editor = await vscode.window.showTextDocument(doc);
await sleep(2000); // Wait for server activation
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
}
async function sleep(ms: number) {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
}
アクティベーション部分では
package.jsonで定義されている{publisher.name}.{extensionId}を使用して拡張機能を取得します。- 指定されたドキュメントを開き、アクティブなテキストエディターに表示します。
- 言語サーバーがインスタンス化されていることを確認するために、2秒間スリープします。
準備ができた後、各言語機能に対応するVS Code コマンドを実行し、返された結果をアサートできます。
実装したばかりの診断機能をカバーするテストがもう1つあります。client/src/test/diagnostics.test.ts で確認してください。
高度なトピック
これまで、このガイドでは
- 言語サーバーと言語サーバープロトコルの概要。
- VS Code における言語サーバー拡張機能のアーキテクチャ
- lsp-sample 拡張機能、およびその開発/デバッグ/検査/テスト方法について説明しました。
このガイドには収まらなかった、より高度なトピックがいくつかあります。言語サーバー開発のさらなる学習のために、これらのリソースへのリンクを含めます。
追加の言語サーバー機能
以下の言語機能は、コード補完とともに言語サーバーで現在サポートされています。
- ドキュメントハイライト: テキストドキュメント内のすべての「等しい」記号をハイライト表示します。
- ホバー: テキストドキュメントで選択された記号のホバー情報を提供します。
- 署名ヘルプ: テキストドキュメントで選択された記号の署名ヘルプを提供します。
- 定義へ移動: テキストドキュメントで選択された記号の定義へ移動サポートを提供します。
- 型定義へ移動: テキストドキュメントで選択された記号の型/インターフェース定義へ移動サポートを提供します。
- 実装へ移動: テキストドキュメントで選択された記号の実装定義へ移動サポートを提供します。
- 参照の検索: テキストドキュメントで選択された記号のプロジェクト全体のすべての参照を検索します。
- ドキュメントシンボルのリスト: テキストドキュメントで定義されたすべてのシンボルをリスト表示します。
- ワークスペースシンボルのリスト: プロジェクト全体のすべてのシンボルをリスト表示します。
- コードアクション: 特定のテキストドキュメントと範囲に対して実行するコマンド (通常は整形/リファクタリング) を計算します。
- CodeLens: 特定のテキストドキュメントの CodeLens 統計を計算します。
- ドキュメントフォーマット: ドキュメント全体のフォーマット、ドキュメント範囲のフォーマット、入力時のフォーマットが含まれます。
- 名前変更: シンボルのプロジェクト全体の名前変更。
- ドキュメントリンク: ドキュメント内のリンクを計算および解決します。
- ドキュメントカラー: ドキュメント内の色を計算および解決し、エディターでカラーピッカーを提供します。
プログラムによる言語機能のトピックでは、上記の各言語機能について説明し、言語サーバープロトコルを介して、または拡張機能から直接拡張 API を使用して実装する方法についてガイダンスを提供します。
増分テキストドキュメント同期
この例では、vscode-languageserver モジュールが提供するシンプルなテキストドキュメントマネージャーを使用して、VS Code と言語サーバーの間でドキュメントを同期しています。
これには2つの欠点があります。
- テキストドキュメントのコンテンツ全体が繰り返しサーバーに送信されるため、大量のデータが転送されます。
- 既存の言語ライブラリを使用する場合、そのようなライブラリは通常、不要な解析や抽象構文木の作成を避けるために増分ドキュメント更新をサポートしています。
したがって、プロトコルは増分ドキュメント同期もサポートしています。
増分ドキュメント同期を利用するには、サーバーは3つの通知ハンドラーをインストールする必要があります。
- onDidOpenTextDocument: VS Code でテキストドキュメントが開かれたときに呼び出されます。
- onDidChangeTextDocument: VS Code でテキストドキュメントの内容が変更されたときに呼び出されます。
- onDidCloseTextDocument: VS Code でテキストドキュメントが閉じられたときに呼び出されます。
以下は、これらの通知ハンドラーを接続にフックし、初期化時に適切な機能を返す方法を示すコードスニペットです。
connection.onInitialize((params): InitializeResult => {
...
return {
capabilities: {
// Enable incremental document sync
textDocumentSync: TextDocumentSyncKind.Incremental,
...
}
};
});
connection.onDidOpenTextDocument((params) => {
// A text document was opened in VS Code.
// params.uri uniquely identifies the document. For documents stored on disk, this is a file URI.
// params.text the initial full content of the document.
});
connection.onDidChangeTextDocument((params) => {
// The content of a text document has change in VS Code.
// params.uri uniquely identifies the document.
// params.contentChanges describe the content changes to the document.
});
connection.onDidCloseTextDocument((params) => {
// A text document was closed in VS Code.
// params.uri uniquely identifies the document.
});
/*
Make the text document manager listen on the connection
for open, change and close text document events.
Comment out this line to allow `connection.onDidOpenTextDocument`,
`connection.onDidChangeTextDocument`, and `connection.onDidCloseTextDocument` to handle the events
*/
// documents.listen(connection);
VS Code API を直接使用して言語機能を実装する
言語サーバーには多くの利点がありますが、VS Code の編集機能を拡張する唯一の選択肢ではありません。ある種類のドキュメントにいくつかの簡単な言語機能を追加したい場合は、vscode.languages.register[LANGUAGE_FEATURE]Provider をオプションとして検討してください。
completions-sample は、vscode.languages.registerCompletionItemProvider を使用して、プレーンテキストファイルにいくつかのスニペットを補完として追加する例です。
VS Code API の使用法を示すその他のサンプルは、https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-extension-samples で見つけることができます。
言語サーバー用のエラー許容パーサー
ほとんどの場合、エディターのコードは不完全で構文的に誤っていますが、開発者はオートコンプリートやその他の言語機能が機能することを期待します。したがって、言語サーバーにはエラー許容パーサーが必要です。パーサーは部分的に完成したコードから意味のある AST を生成し、言語サーバーは AST に基づいて言語機能を提供します。
VS Code で PHP サポートを改善していたとき、公式の PHP パーサーがエラー許容ではなく、言語サーバーで直接再利用できないことに気づきました。そこで、私たちはMicrosoft/tolerant-php-parser に取り組み、エラー許容パーサーを実装する必要がある言語サーバーの作成者に役立つ可能性のある詳細なメモを残しました。
よくある質問
サーバーにアタッチしようとすると、「ランタイムプロセスに接続できません (5000 ミリ秒後にタイムアウト)」というエラーが表示されます。
デバッガーをアタッチしようとしたときにサーバーが実行されていない場合、このタイムアウトエラーが表示されます。クライアントは言語サーバーを開始するため、実行中のサーバーがあることを確認するためにクライアントを開始していることを確認してください。サーバーの起動を妨げている場合は、クライアントのブレークポイントを無効にする必要がある場合もあります。
このガイドとLSP 仕様を読みましたが、まだ未解決の質問があります。どこで助けを得られますか?
https://github.com/microsoft/language-server-protocol で課題を開いてください。